|
SLOVENSKI STANDARD
01-januar-2023
Kakovost zraka v kabini civilnih letal - Kemijske spojine
Cabin air quality on civil aircraft - Chemical compounds
Kabinenluftqualität in Verkehrsflugzeugen - Chemische Parameter
Qualité de l'air en cabine d'avions civils - Composés chimiques
Ta slovenski standard je istoveten z: CEN/TR 17904:2022
ICS:
13.040.01 Kakovost zraka na splošno Air quality in general
49.095 Oprema za potnike in Passenger and cabin
oprema kabin equipment
2003-01.Slovenski inštitut za standardizacijo. Razmnoževanje celote ali delov tega standarda ni dovoljeno.
CEN/TR 17904
TECHNICAL REPORT
RAPPORT TECHNIQUE
November 2022
TECHNISCHER REPORT
ICS 49.095
English Version
Cabin air quality on civil aircraft - Chemical compounds
Qualité de l'air en cabine d'avions civils ¿ Composés Kabinenluftqualität in Verkehrsflugzeugen - Chemische
chimiques Parameter
This Technical Report was approved by CEN on 30 October 2022. It has been drawn up by the Technical Committee CEN/TC 436.
CEN members are the national standards bodies of Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia,
Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway,
Poland, Portugal, Republic of North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Türkiye and
United Kingdom.
EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION
COMITÉ EUROPÉEN DE NORMALISATION
EUROPÄISCHES KOMITEE FÜR NORMUNG
CEN-CENELEC Management Centre: Rue de la Science 23, B-1040 Brussels
© 2022 CEN All rights of exploitation in any form and by any means reserved Ref. No. CEN/TR 17904:2022 E
worldwide for CEN national Members.
Contents Page
European foreword . 5
Introduction . 6
1 Scope . 7
2 Normative references . 7
3 Terms and definitions . 7
4 Cabin air quality — chemical compounds . 11
4.1 Chemical compounds in cabin air . 11
4.2 Sources of chemical compounds. 11
4.3 Sources of engine oil leakage in the bleed air system . 11
4.4 Fume event . 12
4.5 Marker compounds . 12
4.6 Environmental control systems (ECS) . 12
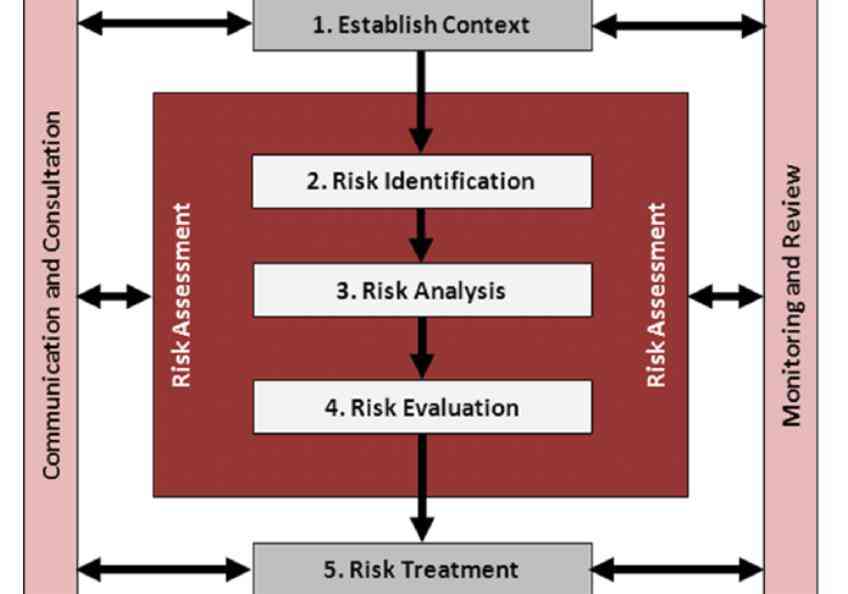
5 Precautionary Principle and hierarchy of controls . 12
5.1 General. 12
5.2 Precautionary Principle . 13
5.3 Hierarchy of controls . 13
5.4 Elimination measures . 14
5.5 Mitigation measures . 14
6 Filtration . 15
6.1 General. 15
6.2 Recirculation cabin air filtration. 15
6.3 Catalytic conversion filtration . 16
7 Air monitoring . 16
7.1 General. 16
7.2 Air monitoring planning/development . 17
7.2.1 Overview . 17
7.2.2 Overview of sampling environment and objectives . 17
7.2.3 Defining flight phases and whether occupied or unoccupied . 17
Table 1 — Possible aircraft system configuration settings by flight phase . 18
7.2.4 Defining sampling locations. 18
7.3 Air monitoring methodology . 19
7.3.1 Real-time monitoring . 19
7.3.2 Time-integrated monitoring . 19
8 Preventative and corrective actions . 21
8.1 General. 21
8.2 Preventative measures pre-flight . 21
8.3 Corrective measures in-flight . 21
8.4 Corrective measures post-flight . 22
8.5 Aircraft Maintenance Manual (AMM) . 22
9 Monitoring of air crew and passengers . 22
9.1 Monitoring air crew . 22
9.2 Monitoring passengers . 23
10 Data compilation, analysis and reporting . 23
10.1 General . 23
10.2 Data compilation . 24
10.2.1 Relevant airline operator reports . 24
10.2.2 Air crew fume event reports . 25
10.3 Analysis and reporting . 26
10.3.1 Analysis . 26
11 Airline worker education and training . 27
11.1 General . 27
11.2 Recommended programme elements, by work group . 27
11.2.1 Programme provisions applicable to pilots, cabin crew and maintenance workers 27
11.2.2 Pilot-specific training and education . 27
11.2.3 Cabin crew-specific training and education . 28
11.2.4 Maintenance worker-specific training and education . 28
Annex A (informative) Environmental Control Systems (ECS) . 29
A.1 General . 29
A.2 Bleed air environmental control systems (ECS) . 29
Figure A.1 — Typical schematic for a bleed air ECS . 30
A.3 Bleed-free environmental control system . 30
Figure A.2 — Typical bleed-free ECS architecture . 31
Annex B (normative) Chemical marker compounds . 32
Table B.1 — Sources of airborne contaminants and their associated chemical marker
compounds . 32
Table B.2 — Reliability ratings for the presence of chemical marker compounds, according
to each source of contamination . 34
Annex C (informative) Precautionary Principle . 37
C.1 Precautionary Principle . 37
C.2 Precautionary Principle considerations: background information . 38
Annex D (informative) Approaches for online monitoring . 40
D.1 General . 40
D.2 Indicative chemical marker compounds . 40
D.3 Pattern recognition . 40
D.4 Differential measurement . 40
Annex E (informative) Reference method for real-time and time-integrated measurement of
chemical marker compounds and (ultra) fine particles . 41
Table E.1 — Examples of standardized methods for real-time and time-integrated
measurements . 41
Table E.2 — Examples of possible methods for real-time measurement of chemical marker
compounds and ultrafine particles . 51
Annex F (informative) Examples of best practice intended to prevent or minimize
contamination . 53
Table F.1 — Examples of best practice for manufacturers, airline operators, pilots and
maintenance operations to prevent or minimize contamination of the aircraft
ventilation supply air system . 53
Annex G (informative) Chemical marker compounds introduced into the cabin . 55
Table G.1 — Chemical marker compounds introduced into the cabin via the outside air to the
ventilation system . 55
Table G.2 — Chemical marker compounds generated within the aircraft cabin environment
................................................................................................................................................................... 57
Annex H (informative) Sources of engine oil leakage into the bleed air system and ventilation
supply air . 58
H.1 Description of oil lubrication system .
...